Some of Your Inquiries:
- What is Market Structure?
- Volumetric Order Blocks
- Liquidity Sweep (X) And Inducement
- Imbalance Concepts
- Supply and demand zones
- Support and resistance
- Sideways or Range-Bound
- HTF Candle
- Trade Examples
- Advantages of Using HSN Algo Indicator
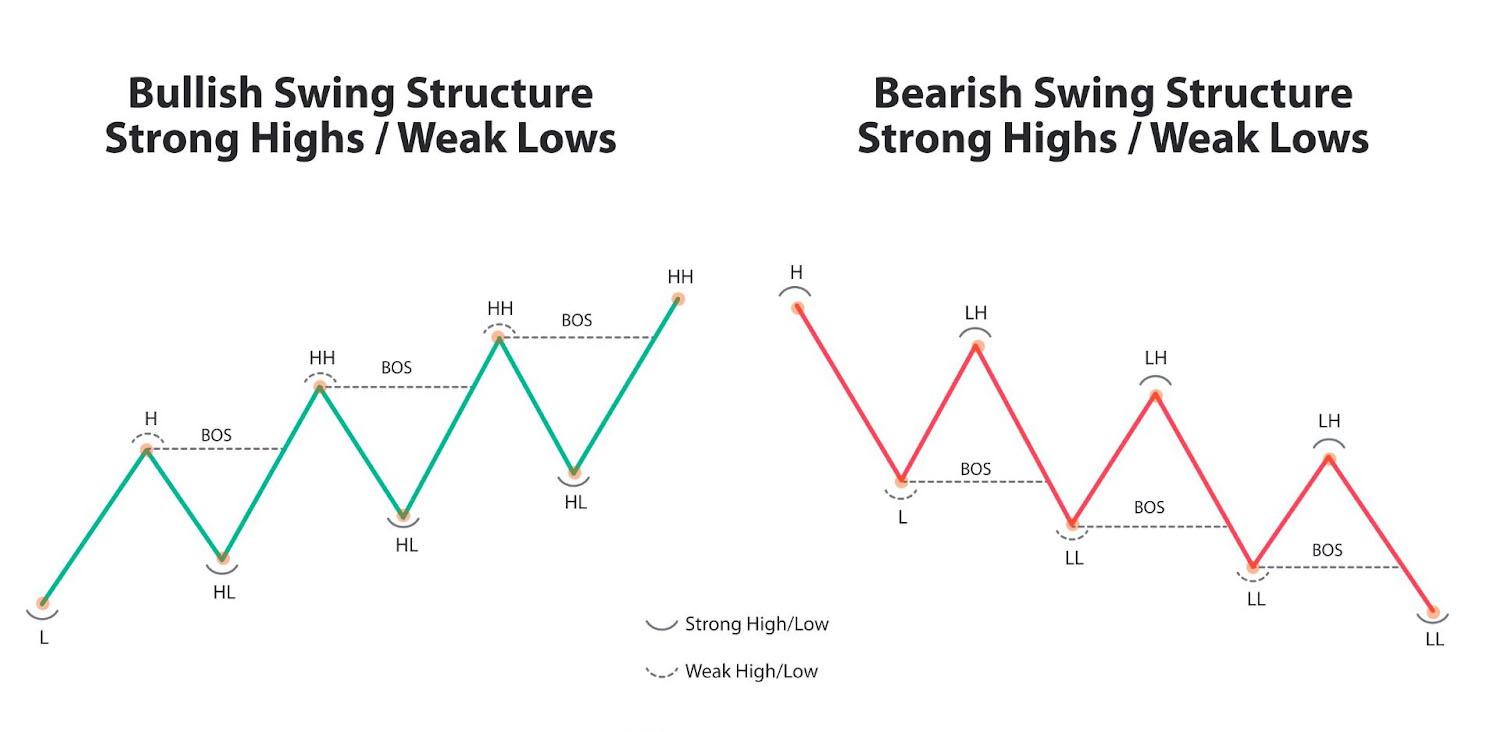
Q. What is Market Structure?
Market structure has been around as long as financial markets. Its core principles are still vital for analyzing price movements and spotting trading opportunities. From bullish moves, to bearish and in between with ranges. Market Structure is often referred to as Price Action.
Market structure helps traders identify trend reversals and trend continuations in the market through two distinct methods:
Change of Character (CHoCH)
Break of Structure (BOS)
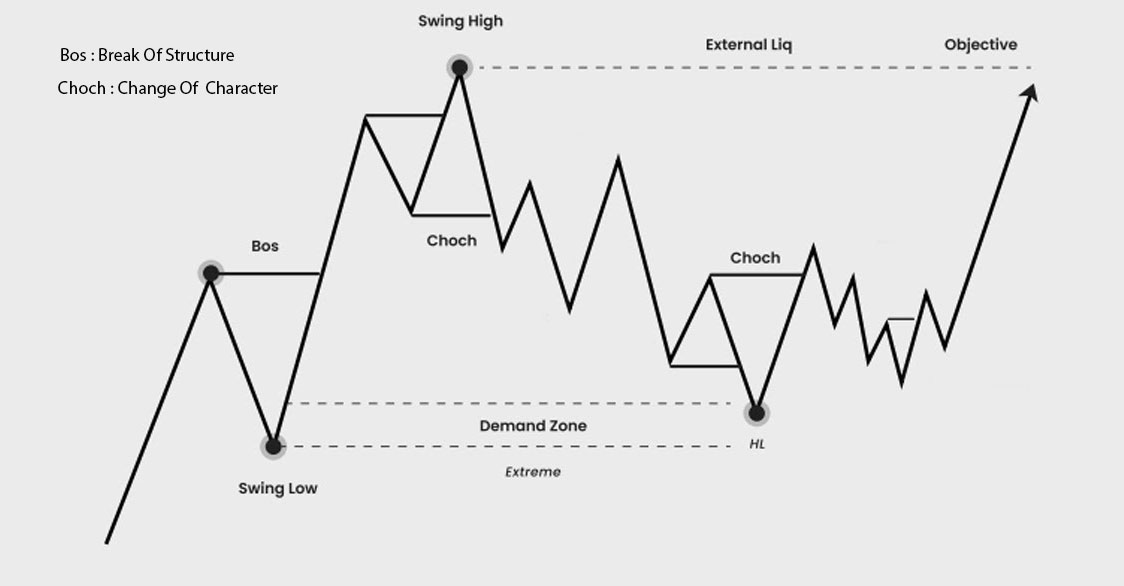
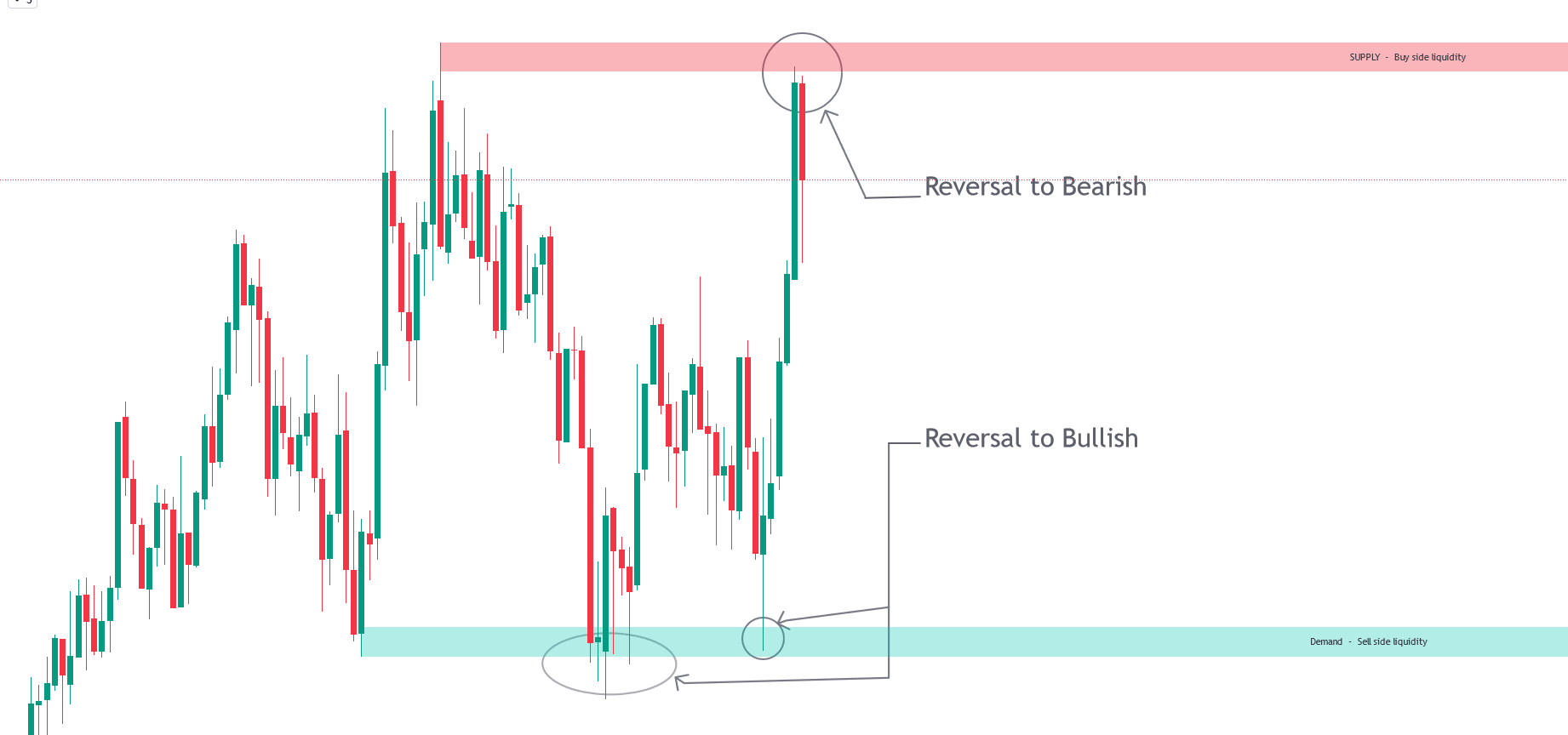
A change of character (CHoCH), also known as a 'market structure shift,' occurs when the price breaks a previous swing low during an uptrend (bullish CHoCH) or a previous swing high during a downtrend (bearish CHoCH). This signals a potential market reversal.
BOS stands for "Break of Structure." It refers to a situation where the price of an asset breaks through a significant support or resistance level, indicating a potential change in the market trend. A BOS can signal the continuation of a trend or the start of a new trend, depending on the context.
For example:
In an uptrend, a BOS occurs when the price breaks above a previous swing high, suggesting the trend will continue.
In a downtrend, a BOS happens when the price breaks below a previous swing low, indicating the downtrend may persist.
Traders use BOS to identify key levels and make informed decisions about entering or exiting positions.
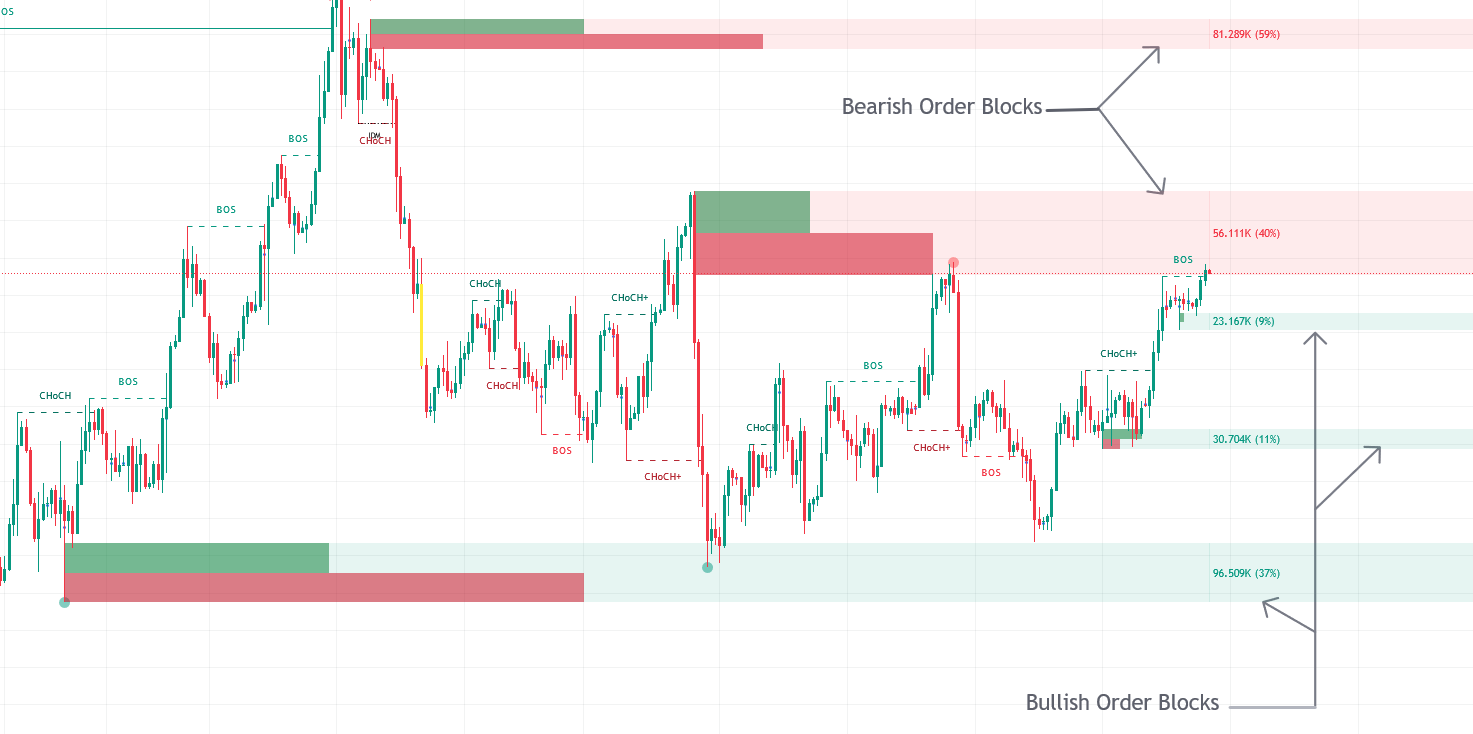
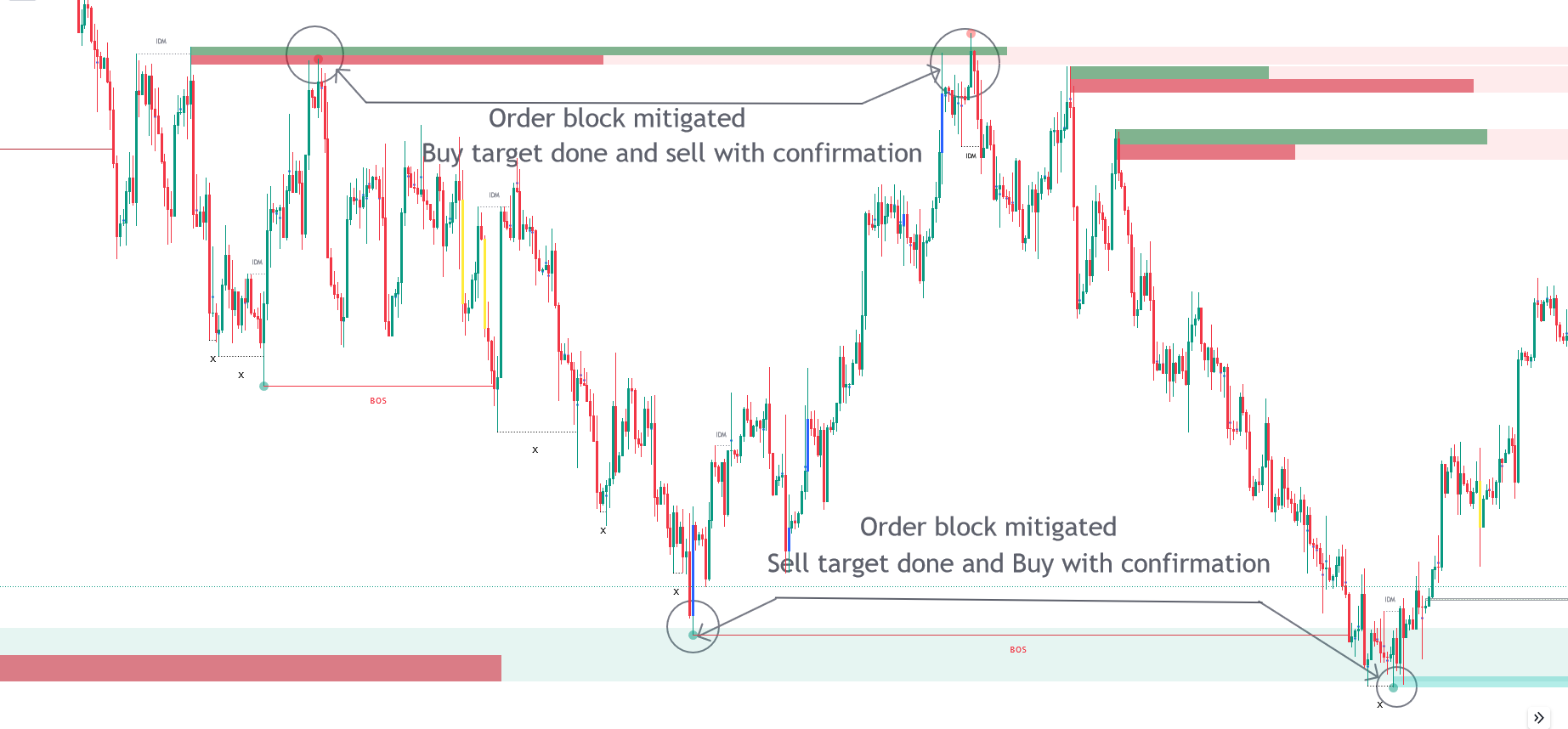
Q.Volumetric Order Blocks
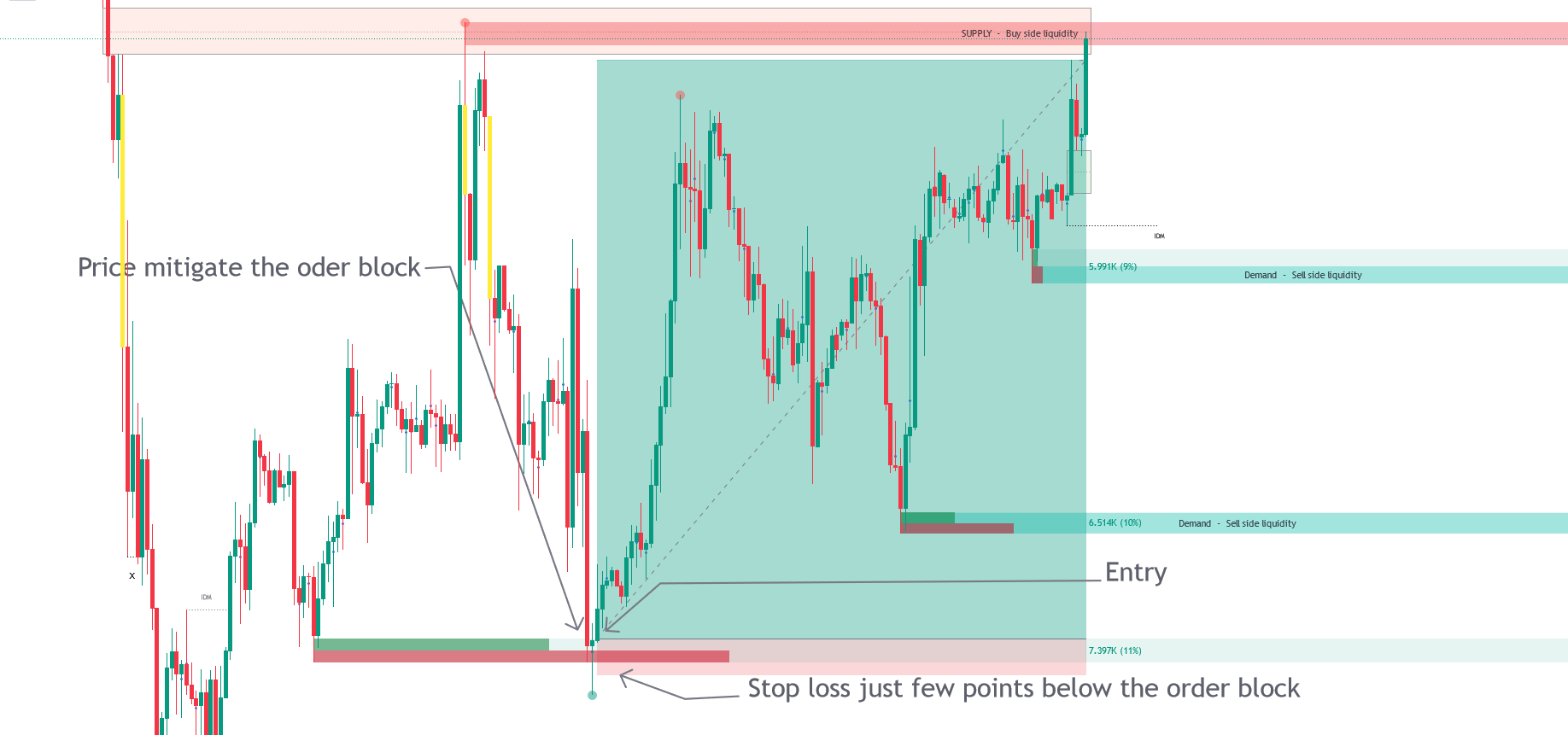
Volumetric Order Blocks show price areas where experienced traders place large orders, acting as potential support or resistance. The toolkit highlights these areas automatically, and they disappear once the orders are filled.
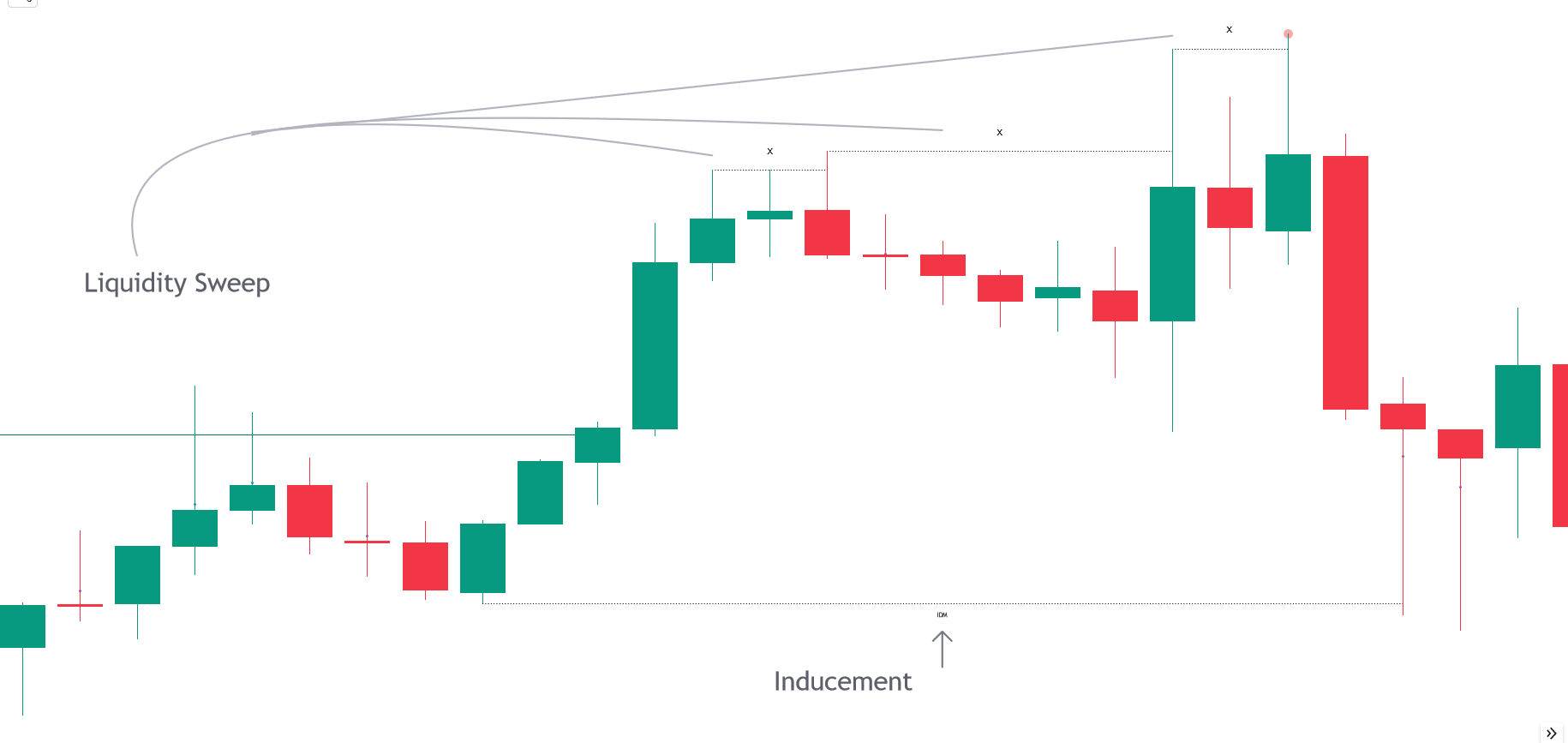
Q. Liquidity Sweep (X) And Inducement
In the context of the Smart Money concept, a liquidity sweep refers to a deliberate move by institutional traders or "smart money" to trigger stop-loss orders and capture liquidity. This involves driving the price to key levels where retail traders have placed stop-loss orders or pending orders (e.g., above resistance or below support). Once these orders are triggered, the smart money can enter or exit positions with less slippage and better prices.
In the context of Smart Money Concepts in trading, an "inducement" refers to a deliberate action taken by institutional or large traders to manipulate the market in order to create favorable conditions for their trading strategies. This manipulation can involve actions such as creating false breakouts, triggering stop-loss orders, or influencing sentiment to achieve desired price movements.
Inducements are often used to deceive retail traders or less informed participants, exploiting their reactions to market movements for the benefit of the smart money. These actions can lead to temporary price spikes or drops that are strategically used to enter or exit positions at optimal prices.
Understanding inducements is crucial for traders aiming to navigate market manipulation and identify genuine market trends and reversals amid orchestrated movements by large participants.
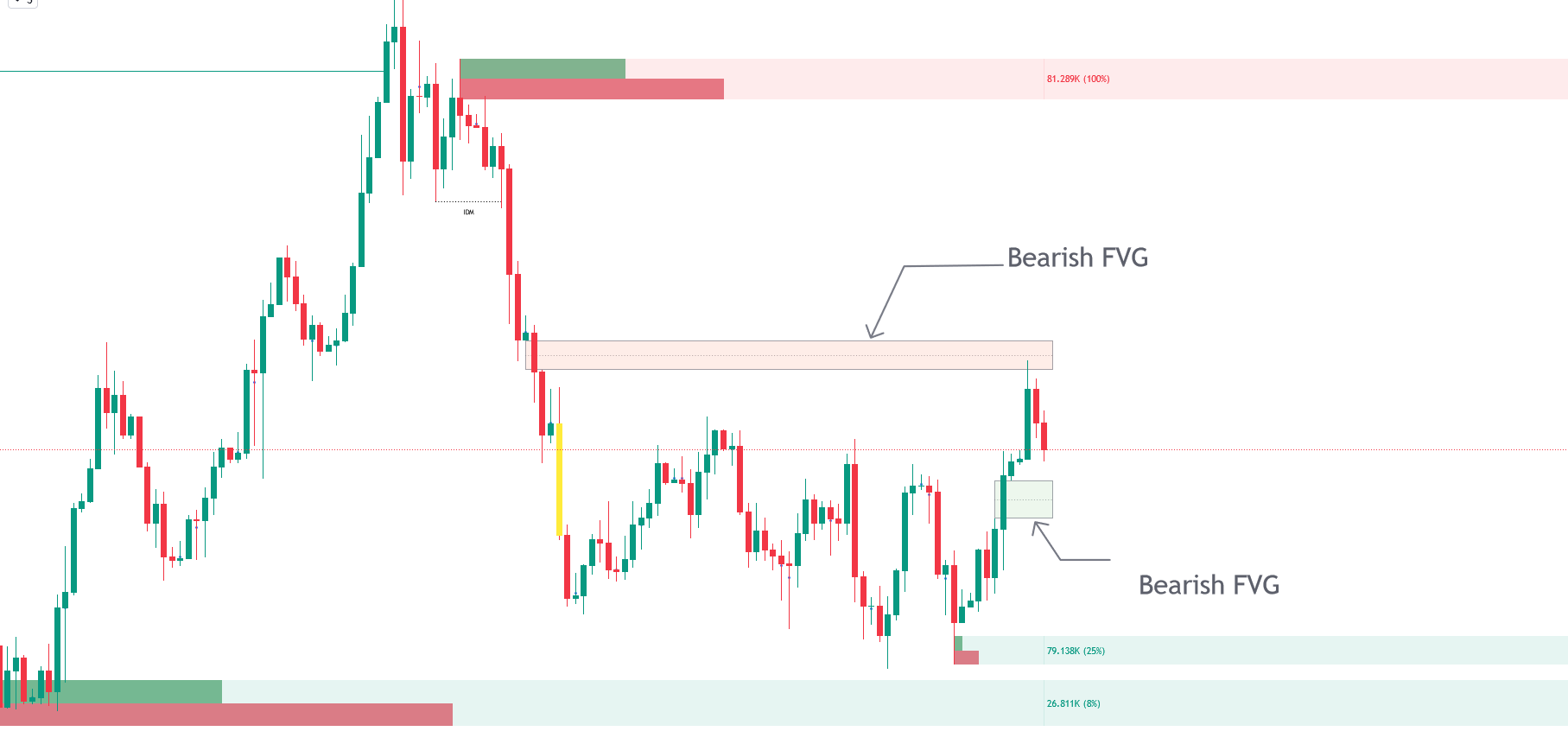
Q. Imbalance Concepts
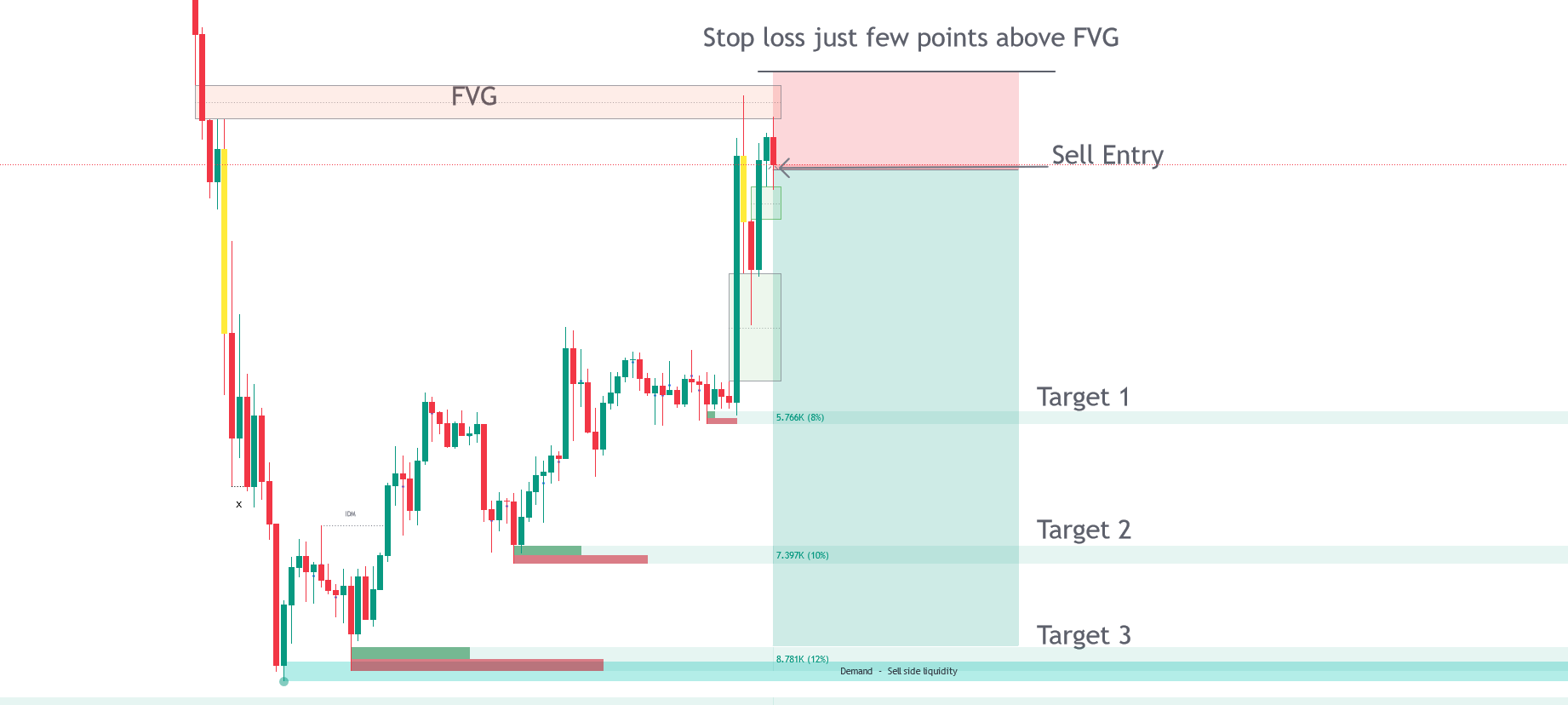
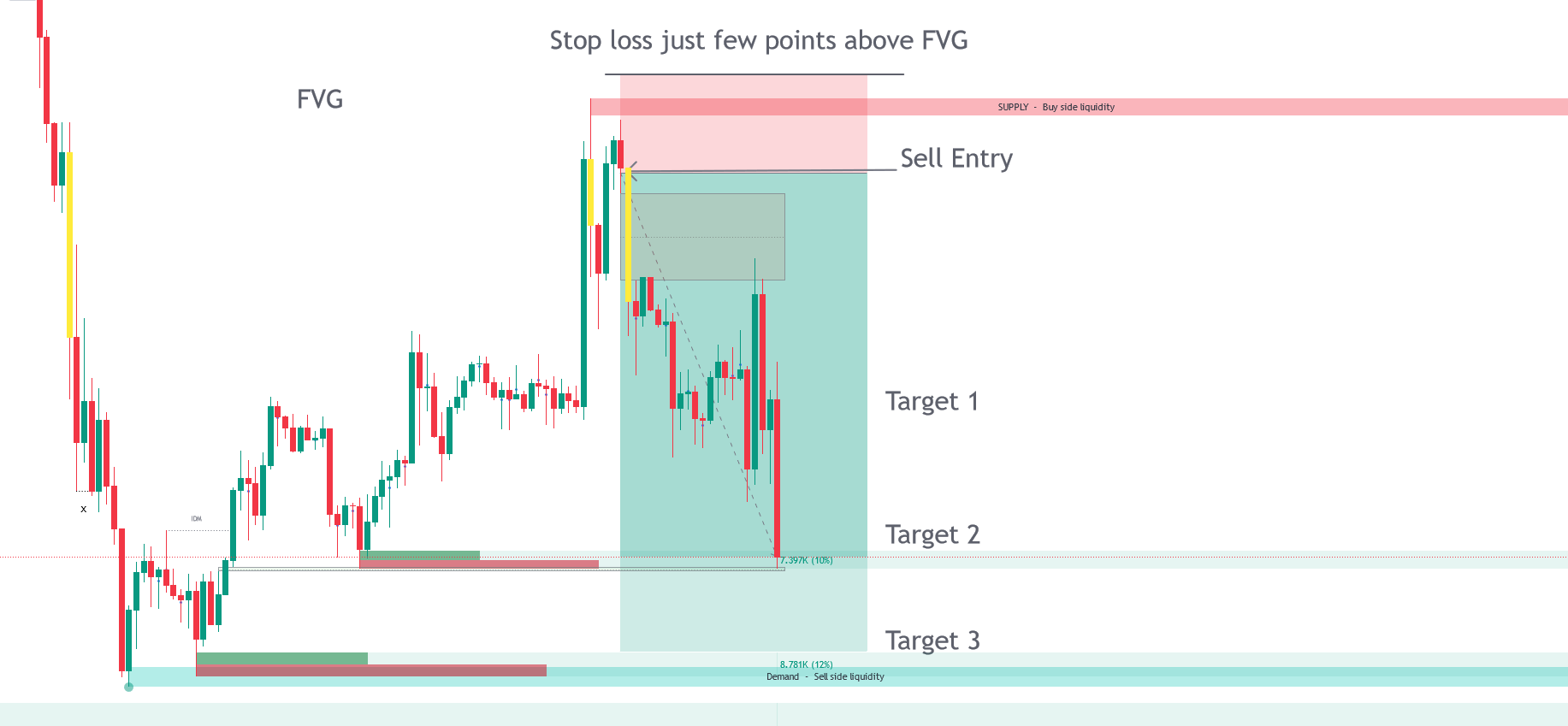
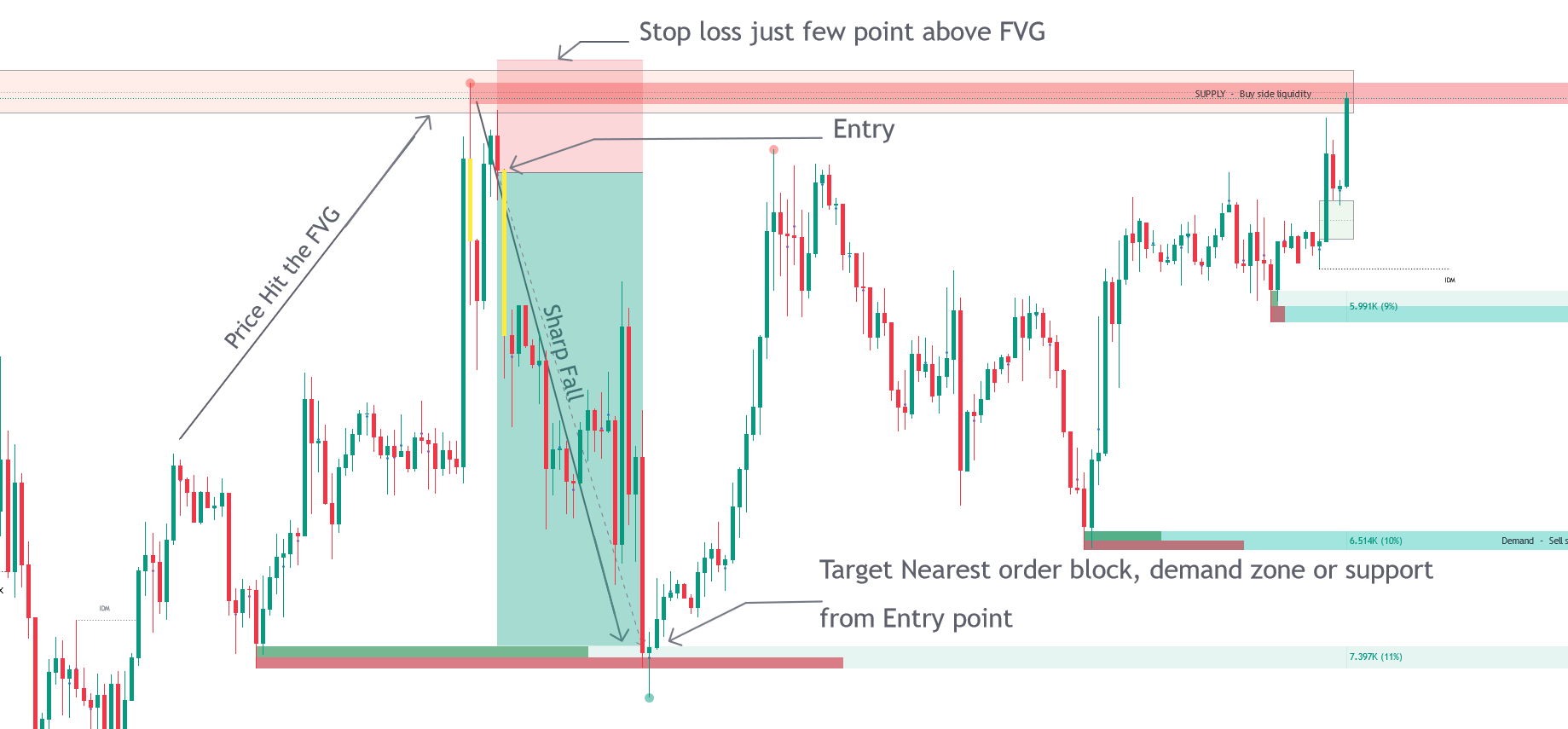
Market imbalance occurs when there is a notable disparity between buying and selling pressures, often leaving unfilled gaps on the chart. These gaps indicate inefficiencies that the market may seek to rectify later, influencing future price actions. The Smart Money Concepts toolkit aids in pinpointing these inefficiencies by: Fair Value Gaps (FVG): These zones highlight where the price may have passed through significant support or resistance levels without adequate buying or selling activity to fill the gap.
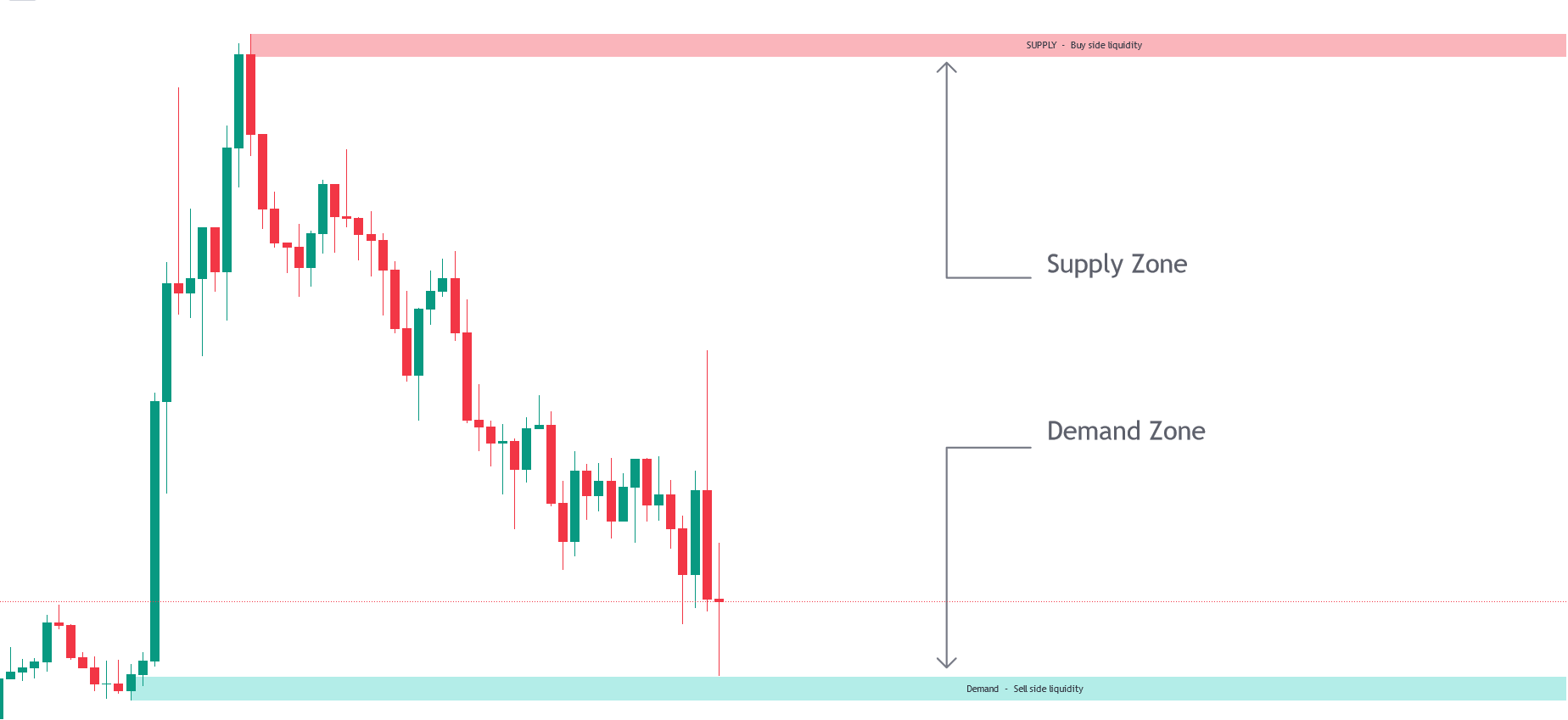
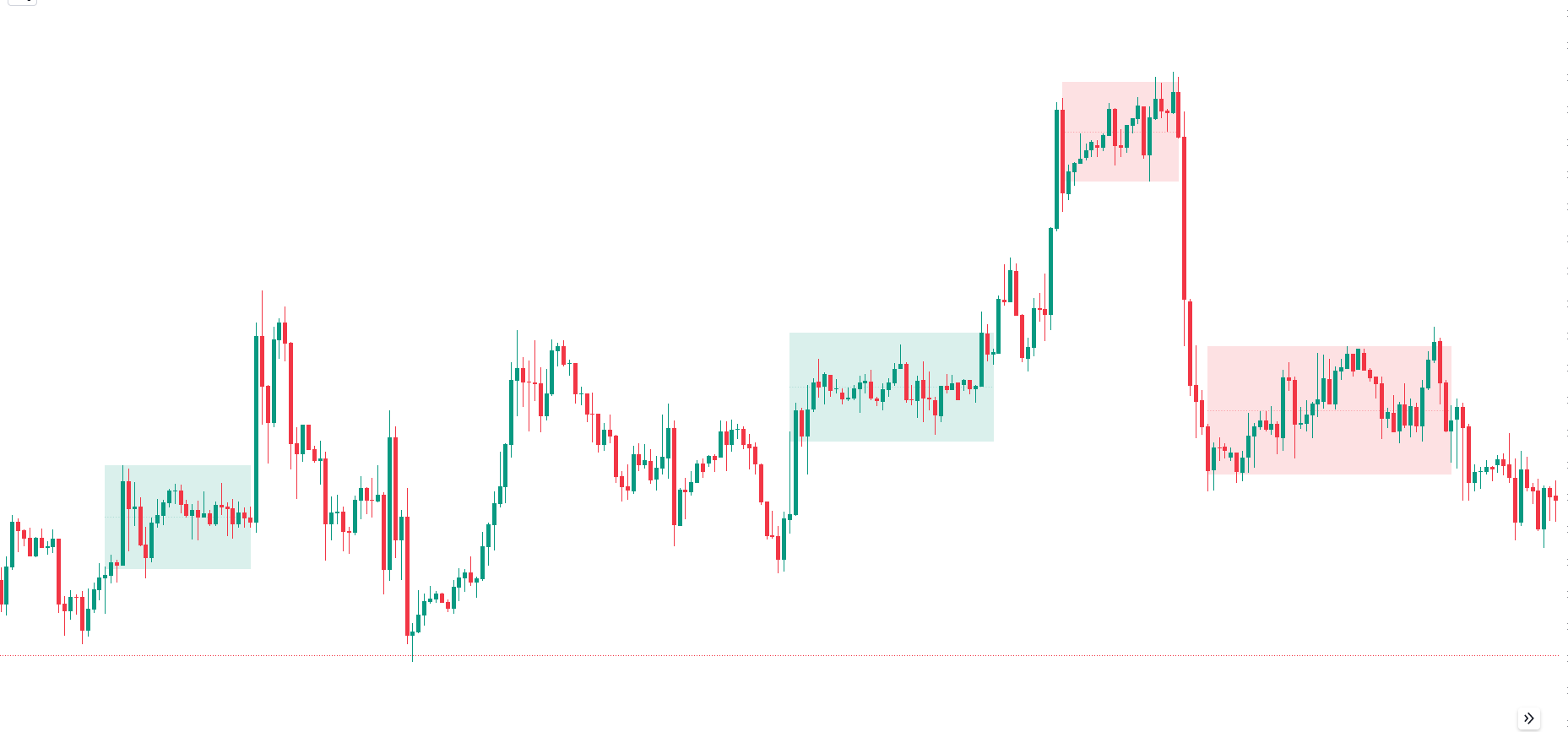
Q. Supply and demand zones
Supply and demand zones in trading are key areas on a price chart where significant buying or selling has previously occurred, often leading to future price reversals or continuations. These zones are used by traders to identify potential entry and exit points.
Example with a Chart
Supply Zone:
Price previously rose to a certain level and then fell sharply.
This level is marked as a supply zone.
When price approaches this zone again, it often encounters resistance and may fall.
Demand Zone:
Price previously fell to a certain level and then rose sharply.
This level is marked as a demand zone.
When price approaches this zone again, it often encounters support and may rise.
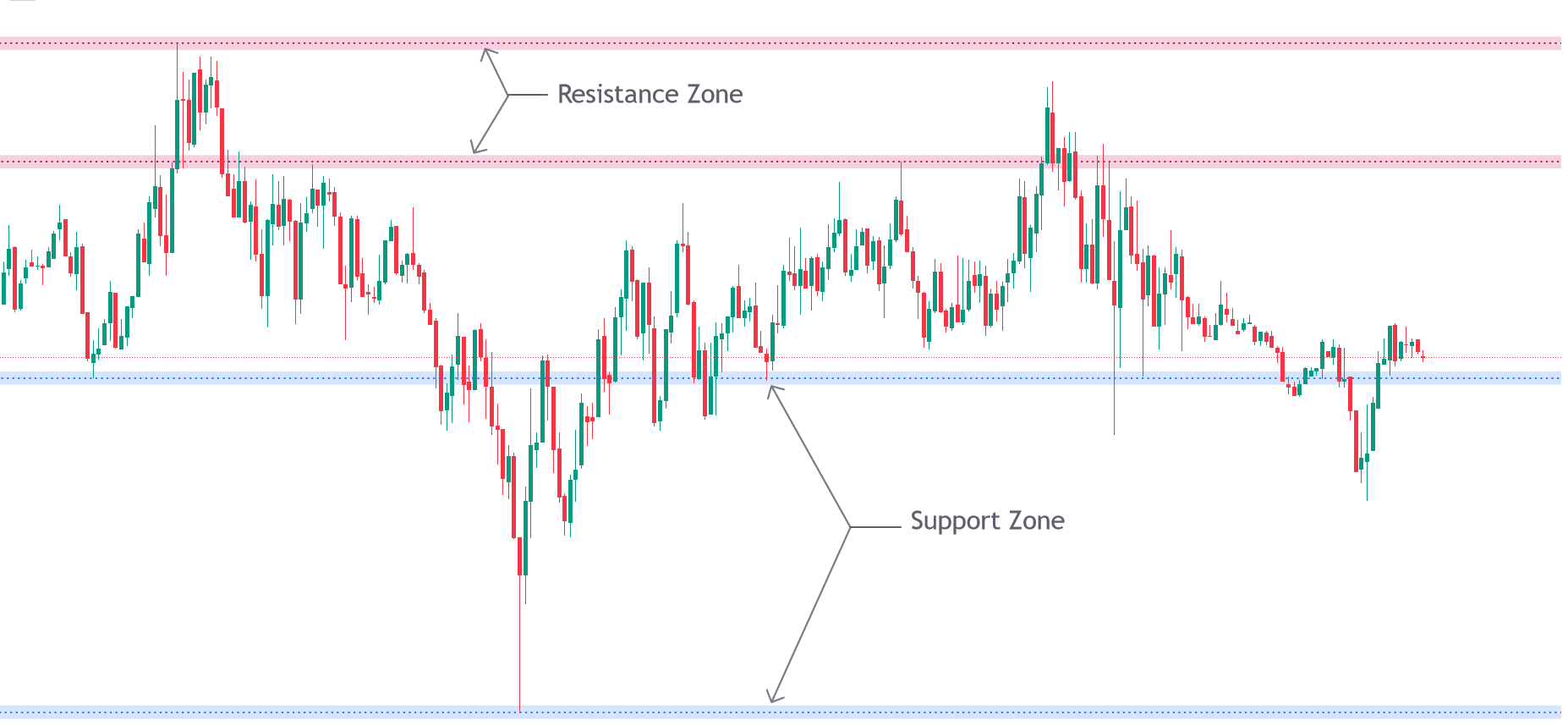
Q. Support and resistance
Support and resistance are fundamental concepts in technical analysis, a method traders use to forecast future price movements by analyzing past market data, primarily price and volume.
Support
Definition: Support is a price level where a downtrend can be expected to pause due to a concentration of demand. As the price of an asset drops, demand for the shares increases, forming a support line.
Function: At this level, buyers tend to enter the market in large enough numbers to prevent the price from falling further. This often happens because traders see it as a good buying opportunity.
Identification: Support levels can be identified using various methods such as historical price levels where the price has repeatedly bounced up, trendlines, moving averages, and technical indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI).
Resistance
Definition: Resistance is a price level where a rising trend can be expected to pause due to a concentration of supply. As the price of an asset increases, selling interest grows, forming a resistance line.
Function: At this level, sellers enter the market in large enough numbers to prevent the price from rising further. Traders often view it as an optimal point to sell or take profits.
Identification: Resistance levels can be determined through previous price highs, trendlines, moving averages, and other technical indicators.
Q. Sideways or Range-Bound
In trading, "sideways" or "range" refers to a market condition where the price of an asset fluctuates within a relatively narrow range without a clear trend in either direction. During such periods, the asset's price moves up and down between a defined support level (the lower boundary) and a resistance level (the upper boundary), creating a horizontal or sideways pattern on a price chart.
Understanding and recognizing a sideways or range-bound market is crucial for traders, this add on help to adopt appropriate strategies and avoid losses from false trend signals.
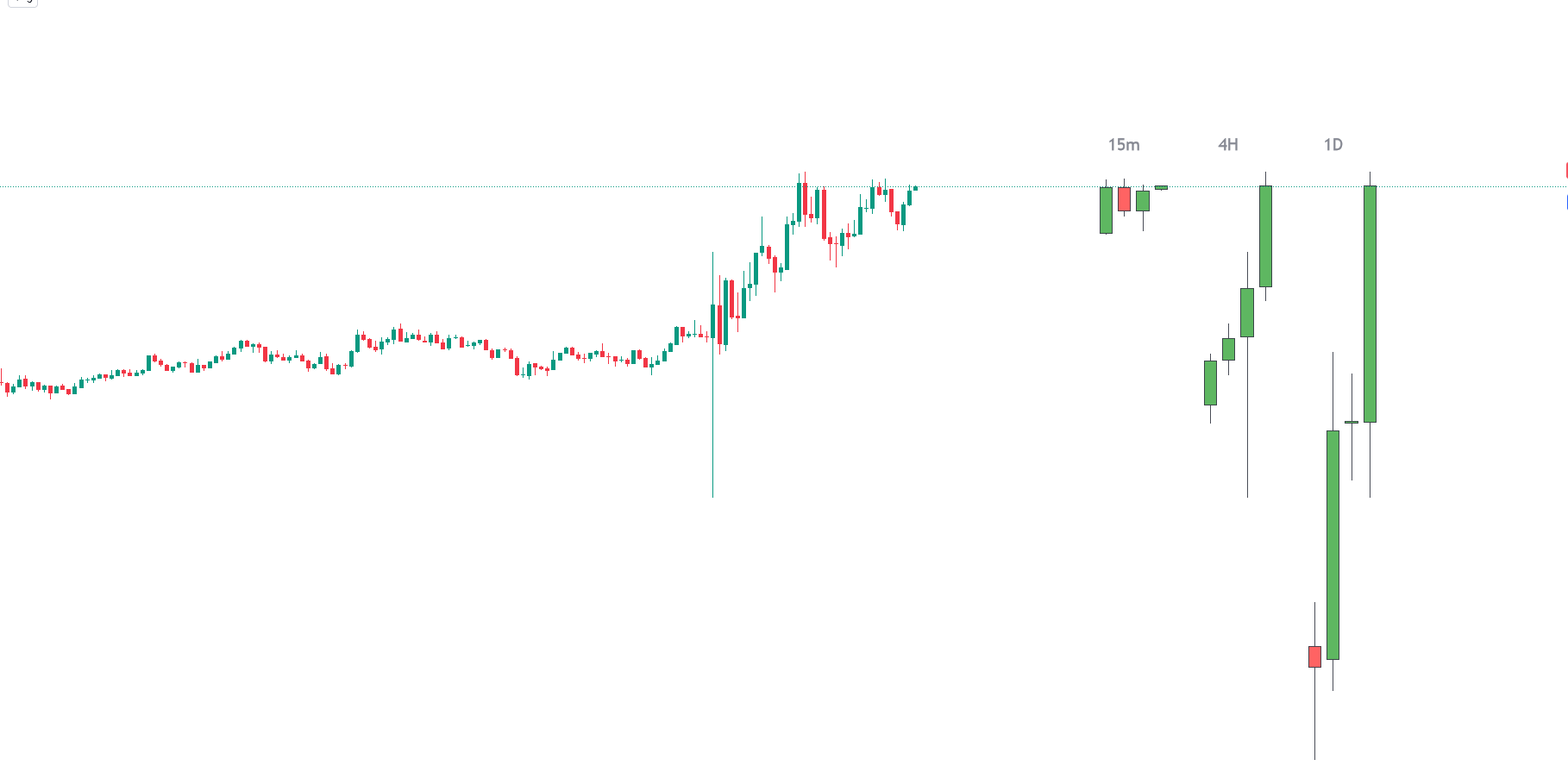
Q. HTF Candle
The HTF Candle Insights indicator assists traders in observing larger time frames (HTF) while analyzing smaller ones. This tool provides a comprehensive view of market trends and price movements, enabling smarter trading decisions. It is particularly beneficial for traders who seek to grasp major market trends without frequently switching between different chart timeframes.
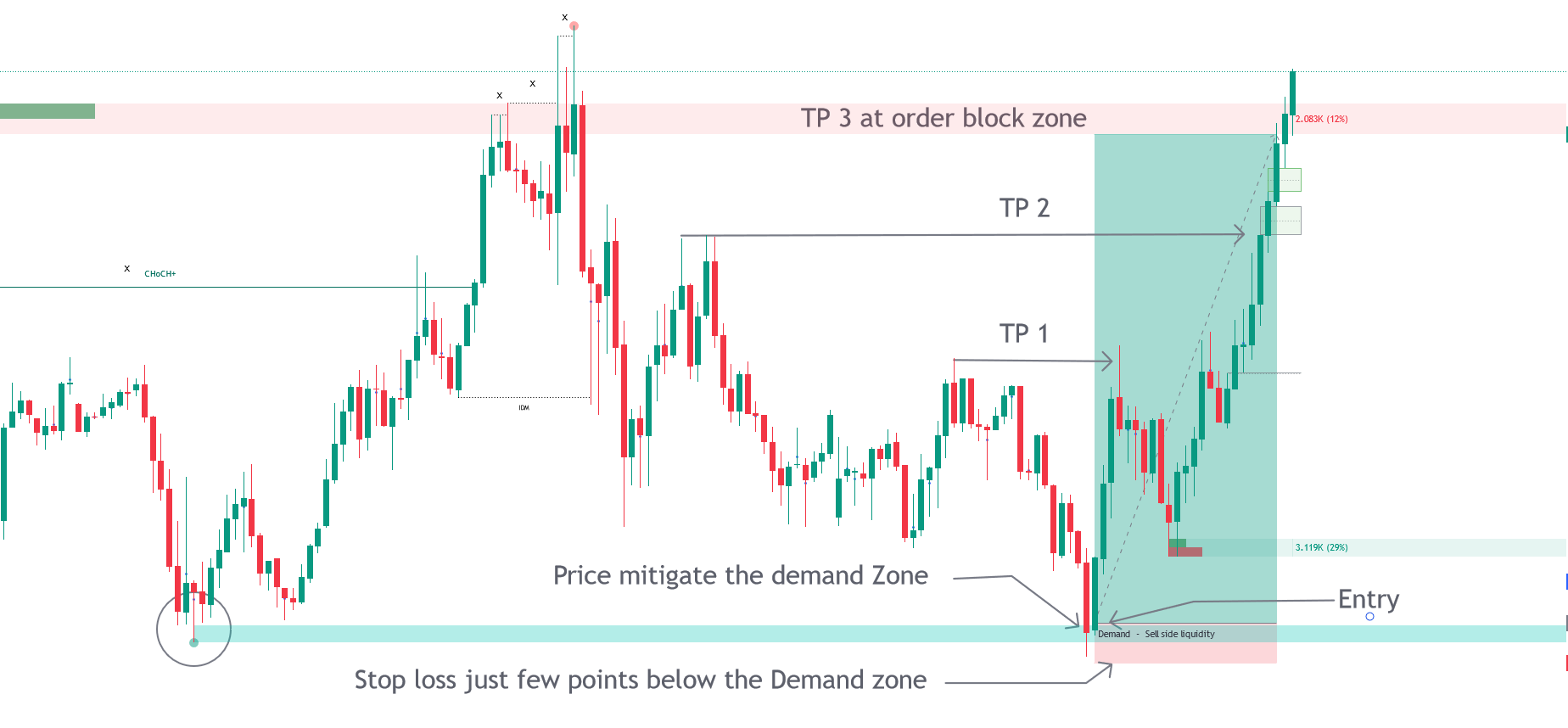
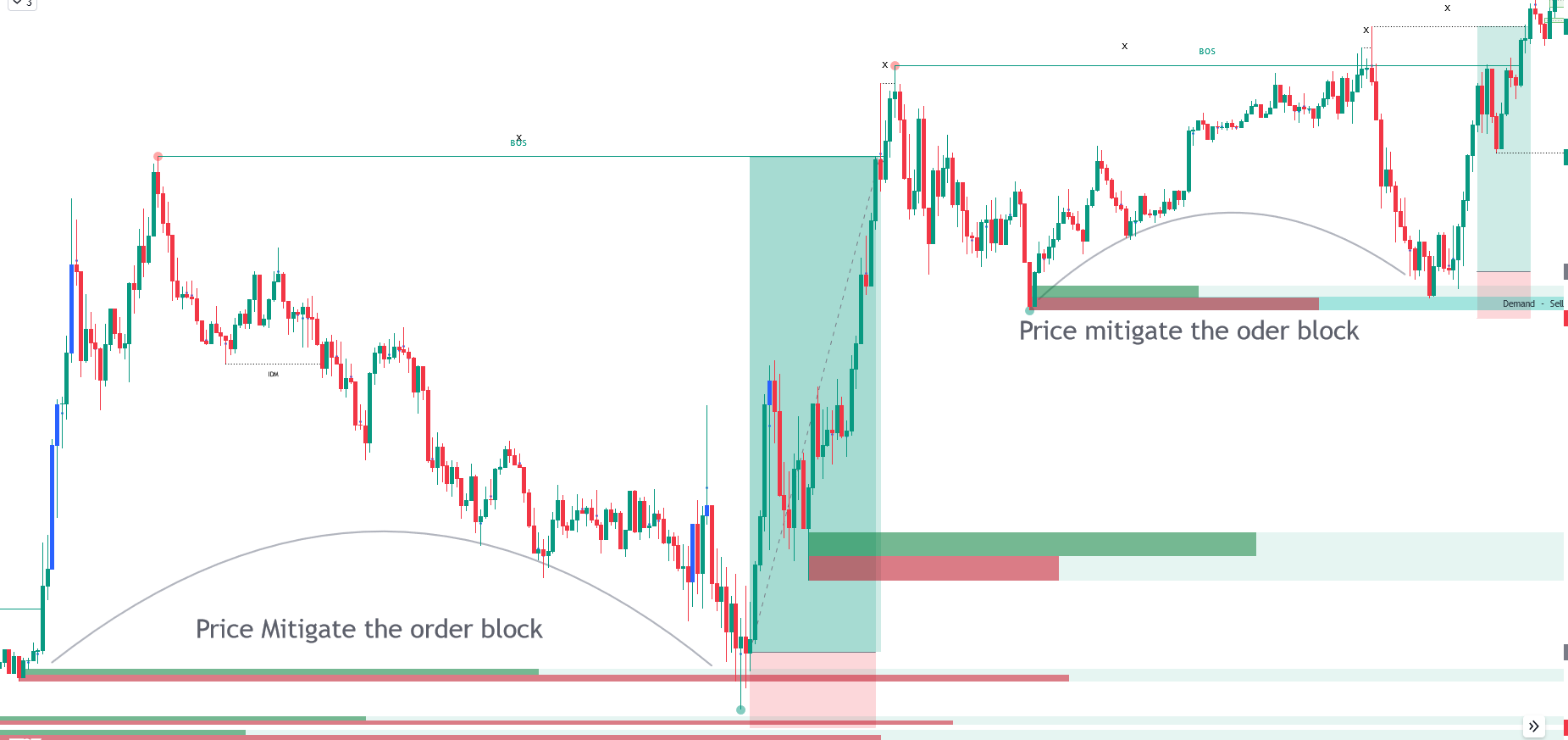
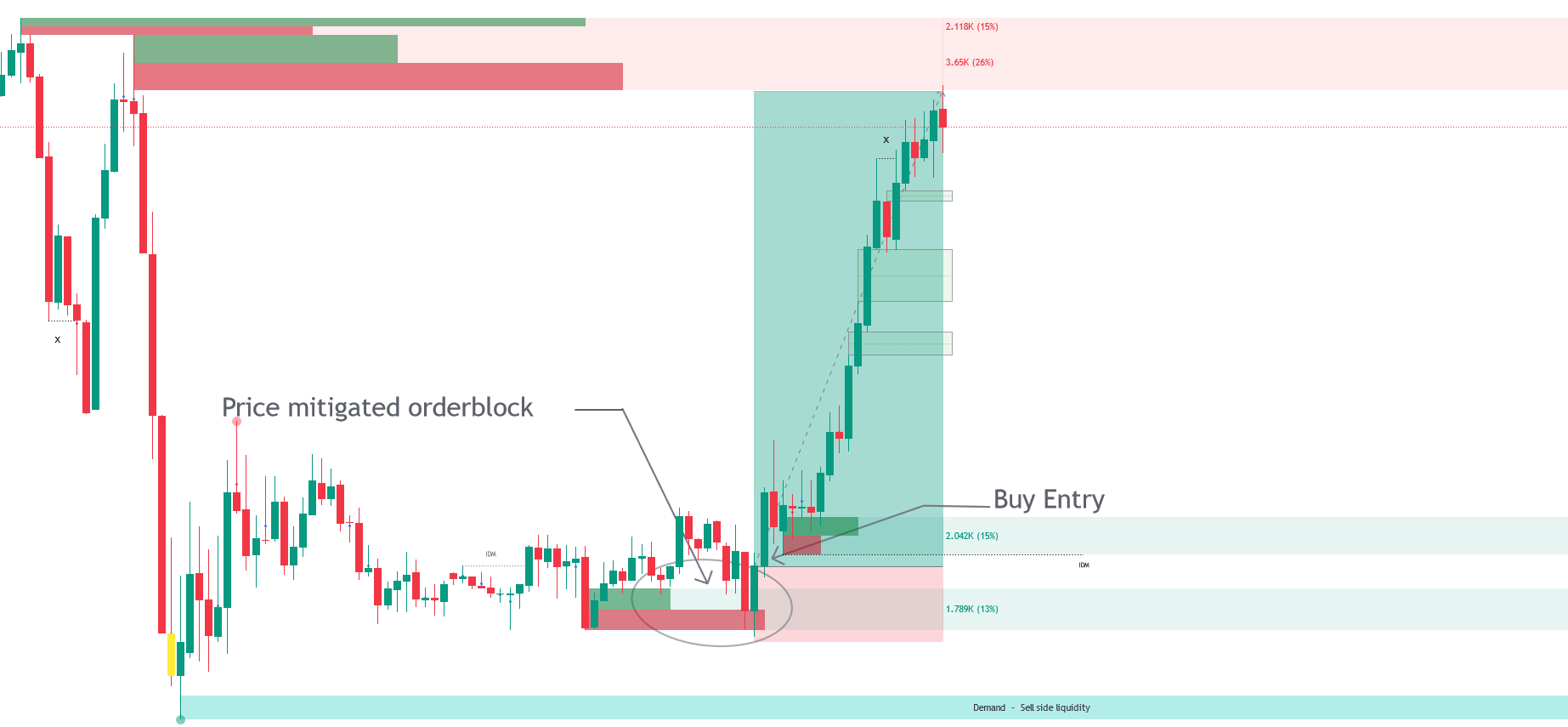
Q. Trade Examples
Trade Entry with Demand zone.
Trade Entry with Bullish Order Block.
Trade Entry with FVG.
Other Examples.
Q. Advantages of Using HSN Algo Indicator
HSN Algo Indicator is purly based on Price Action and Smart Money Concepts (SMC) in trading refer to strategies that follow the actions of big, institutional investors. Here's a simple explanation of the advantages:
Better Market Insight: You get a clearer idea of market trends by following what big investors are doing.
Improved Timing: You can time your trades better by knowing when institutional investors are likely to buy or sell.
Higher Profit Potential: Aligning your trades with big investors can lead to bigger price movements and more profit.
Enhanced Risk Management: Smart money strategies often include strong risk management, helping you protect your investments.
Increased Confidence: Knowing you're following the moves of experienced professionals can boost your trading confidence.
Less Market Noise: You can focus on significant price movements and avoid getting misled by minor fluctuations.
Market Structure Understanding: You learn about key market phases like accumulation and distribution, giving you a better grasp of price action.
Adaptability: These strategies work well in various market conditions, whether it's trending or volatile.
earning from Experts: By studying these methods, you learn advanced techniques used by successful traders.
Long-Term Success: SMC focuses on steady, sustainable growth, avoiding the pitfalls of risky, short-term strategies..